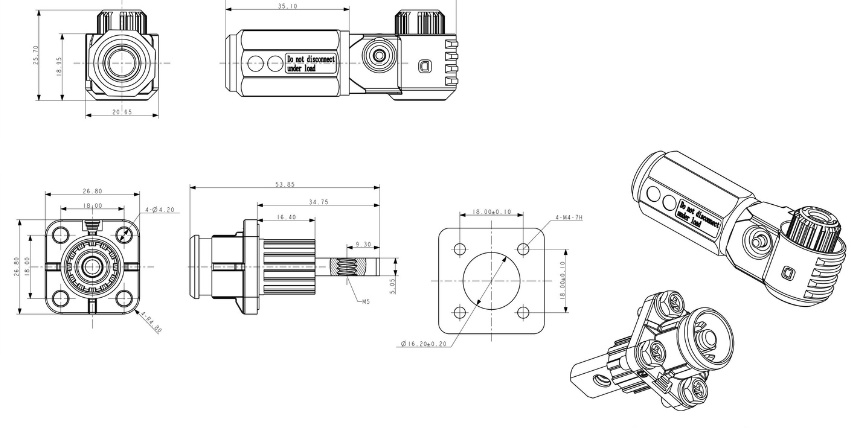
Lithium battery terminals link power to devices. They help run cars, computers, and more. To understand them, dive into this guide. Get smart about how to use, maintain, and choose them right.
What are Battery Terminal Connectors?
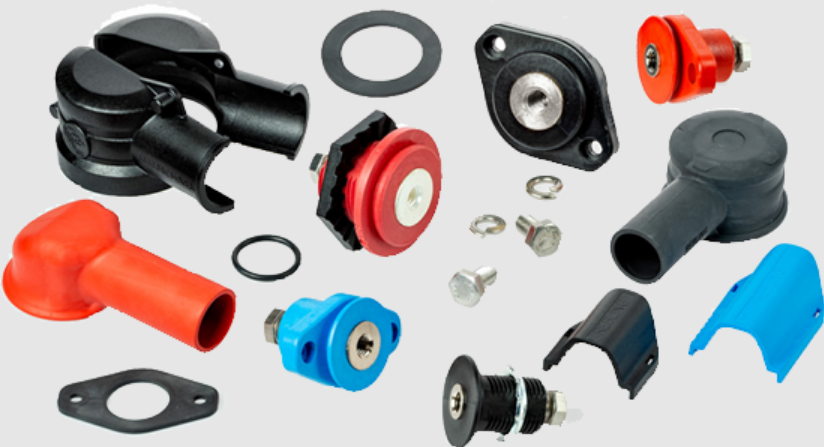

Image Source: www.rebling.com
In the realm of battery technology, battery terminal connectors are critical. In lithium ion battery systems, there exist two such connectors – the battery terminals positive and negative. On one side, the positive terminal connects to the cathode of the battery.
Then, the negative terminal connects to the battery’s anode. A safe and secure connection is vital for a battery’s efficient operation. Hence, top-quality terminal connectors contribute to the durability of lithium batteries.
Applications of Lithium Batteries
o Electric Vehicles
Lithium batteries find extensive use in electric vehicles (EVs). Specially designed terminals in lithium batteries contribute to the efficient power supply. Hence, EVs can drive longer distances with fewer charges.
o Energy Storage
In energy storage systems, lithium batteries stand out. Solid terminal connectors ensure that power is stored effectively. This quality makes lithium batteries valuable in renewable energy technologies.
o Portable Electronics
Portable electronics like smartphones and laptops rely on lithium batteries. Robust terminals enable these devices to run smoothly for longer periods. Users thus enjoy improved device performance.
o Medical Devices
Many medical devices like pacemakers use lithium batteries. Reliable terminals provide the steady power flow these devices need. That way, patient safety and device efficacy are upheld.
o Aerospace Technology
Lithium batteries power a host of aerospace technologies. The high-grade terminals of these batteries ensure a dependable power supply. Consequently, mission-critical systems function without any glitches.
Understanding Battery Terminals!
Purpose of Battery Terminals
– Power Transfer
Lithium battery terminals play a vital role in power transfer. Acting as the gateway, terminals allow power to move from the battery to the device. For instance, in an electric vehicle, terminals facilitate power transfer from the battery to the motor. Thus, a terminal’s health is critical. A damaged terminal can cause inefficient power transfer and even battery failure.
– Connection Point
Besides power transfer, terminals serve as connection points. A lithium battery, like a 200Ah LiFePO4 lithium battery, connects to the device through its terminals. Positive and negative terminals link to their counterparts in the device. Hence, terminal maintenance is crucial. Applying white lithium grease on battery terminals will aid in this upkeep. It reduces corrosion and promotes a robust connection.
– Circuit Completion
Moreover, battery terminals complete the circuit. Current flows from the battery through the device and back via the terminals. This flow is crucial for the device to function. For a lithium-ion cell, the circuit includes the anode, cathode, and terminals. Therefore, ensuring the terminals are clean and corrosion-free ensures a smooth current flow.
– Polarity Identification
Terminals help identify polarity. Each lithium battery has a positive (+) and a negative (-) terminal. Correctly identifying these terminals is key for safe and effective use. Interchanging them can result in serious device damage. Thus, terminals often come marked with ‘+’ and ‘-‘ signs to aid in identification.
– Secure Attachment
In a Lithium battery, terminals serve vital roles. Connectors hold the wires to the battery. Fastening needs to be firm. Looseness leads to weak currents. Terminals also allow for secure detachment when required. Thus, sturdy links ensure effective power flow.
– Electrical Insulation
Next, for safety, battery terminals need electrical insulation. Insulation prevents unwanted electric flow. Electrical shocks may result from non-insulated terminals. A plastic covering often provides this safeguard. Thus, insulation is critical for user safety.
– Corrosion Resistance
Furthermore, terminals resist corrosion. Lithium battery terminals can rust over time. Rusty terminals hinder power flow. Metals like lead or copper combat corrosion. Hence, using these metals improves the battery’s life span.
– Heat Dissipation
Heat dissipation is crucial for battery terminals. Overheating might cause damage. Terminals are often made of metals that disperse heat. Aluminum, for example, is a common choice. Thus, effective heat dissipation prevents damage.
Positive and Negative Terminals: What They Mean?
Lithium battery terminals come in two types. The positive terminal, often marked with a plus, sends power out. The negative terminal, marked with a minus, completes the circuit. Electrical current flows from positive to negative. Color coding helps distinguish between them.
Red typically signifies positive, and black denotes negative. Incorrect connection may lead to damage. Each terminal has a specific function. Both are essential for the battery to work correctly. Understanding the difference ensures safe and proper usage. Proper connection also helps maintain battery health. Hence, knowing terminal polarity is crucial when dealing with Lithium batteries.
Basic Types of Battery Terminals!
o Post Terminals
On Lithium battery terminals, post types often make the cut. Constructed to handle high amps, they’re a staple in car batteries. Nickel, lead, or brass gives strength, enduring constant connect and disconnect cycles. Transferring electricity becomes more seamless with post terminals, a factor of the sizable contact area.
o Stud Terminals
Stud terminals hold great favor in power, marine, and telecommunications industries. Such types bolt wires to terminals, ensuring a secure connection. Torque defines how firm this connection is, usually between 10 to 20 Newton Meters. Safe, resilient, these terminals guarantee steady power flow, even under strenuous conditions.
o Lugs Terminals
Lugs play a pivotal role in battery setups. The design enables cable connection to batteries with ease. For a solid grip, the terminal contains a hole for screw securing. The dimensions, typically 8mm to 10mm, contribute to a solid connection. Considered among the more versatile, lugs are valuable in diverse electrical applications.
o Ring Terminals
Ring terminals feature a round, open-ended design. The configuration ensures easy connection to a stud. Suited for high vibration environments, rings allow cables to hold firm. Sizes can range from 3.5mm to 25.4mm, making them adaptable to varying cable types. From manufacturing to marine applications, ring terminals offer consistent performance.
o Quick Connect
Quick Connect makes connecting and disconnecting wires a breeze. No tools required! The connectors typically range from 2.8mm to 6.3mm, facilitating different wire sizes. In fast-paced setups, Quick Connect terminals ensure a speedy and effective power connection. A time-saver, yes, but also a safety-enhancer!
o Blade Terminals
Blade terminals enable swift power transfer between appliances. With a flat, blade-like design, they fit into sockets effortlessly. Sizes hover between 2.8mm and 9.5mm, suiting varied requirements. Secure, resilient, these terminals find use in appliances, automotive, and electronics.
o Pin Terminals
Pin terminals present an efficient means to connect wires to terminals. With a round pin-like shape, they offer reliable electrical contact. Common dimensions include 2.54mm, 3.96mm, and 5.08mm. Preferred in electronics, audio systems, and control panels, pin terminals ensure sturdy, dependable connections.
o Spade Terminals
Spade terminals feature a fork-like design, securing connections with screws. The opening varies, from 2.8mm to 9.5mm, fitting different bolt sizes. Favored for easy removal and installation, spades find a place in household appliances, electronics, and automotive uses. With spades, a stable, reliable connection is but a few turns away.
| Criteria | Post Terminals | Stud Terminals | Lugs Terminals | Ring Terminals | Quick Connect | Blade Terminals | Spade Terminals |
| Connection Type | Top/Side Mount | Bolt-On | Crimped/Soldered | Bolt-On | Plug-In | Slide-On | Slide-On |
| Current Rating | High (100-200A) | High (100-200A) | Moderate (50-100A) | Moderate (50-100A) | Low (<50A) | Moderate (50-100A) | Low (<50A) |
| Size | Large | Large | Medium | Medium | Small | Small | Small |
| Application | Automotive | Heavy Machinery | Marine/Audio | Electronics | Electronics | Electronics | Electronics |
| Installation Difficulty | Easy | Moderate | Difficult | Moderate | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Durability | High | High | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High | Low | High | High | Moderate | High |
Table on Basic Types of Battery Terminals!
Lithium Battery Terminal Types!
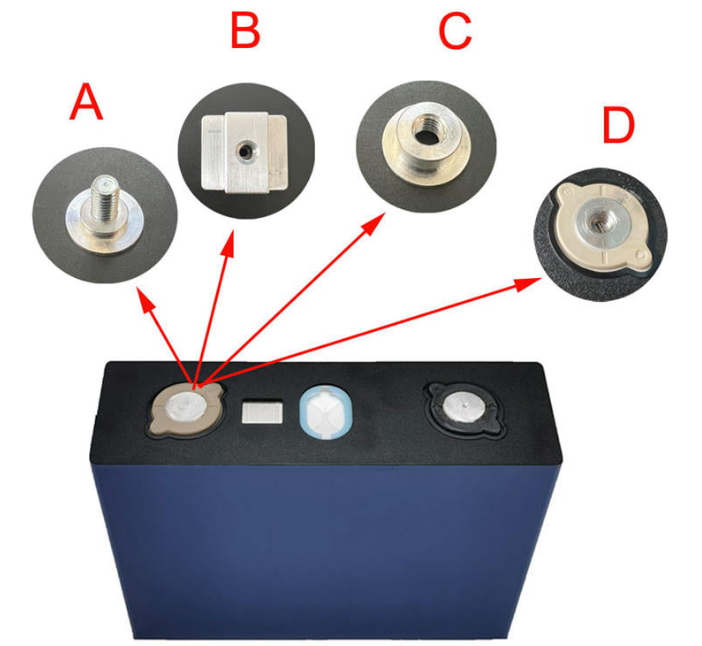
Image Source: www.lythbattery.com
o Nickel Plated
Nickel plated lithium battery terminals offer high electrical conductivity. Nickel, with a resistance of 69.3 nano-ohms per meter, enhances power flow. Second, nickel fights corrosion, adding years to a battery’s lifespan. High-quality, human-made nickel-plated terminals are durable.
o Tin Plated
Tin-plated terminals boost electrical efficiency. The resistance of tin, 109 nano-ohms per meter, ensures smooth power transfer. Besides, tin’s excellent corrosion resistance enhances durability. Tin plated terminals are safe, high-performance options for lithium batteries.
o Gold Plated
In lithium battery connector types, gold-plated ones rank high. Gold’s low resistance, 22.14 nano-ohms per meter, supports superb electricity flow. Moreover, gold doesn’t corrode, offering long-lasting terminal reliability. So, gold-plated terminals represent quality and reliability.
o Pure Copper
Copper terminals, with 16.78 nano-ohms per meter resistance, ensure excellent electrical flow. Copper’s anti-corrosive properties add to terminal lifespan. Pure copper terminals in lithium batteries offer unmatched durability, longevity, and electrical efficiency.
o Brass Terminals
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, provides terminals with moderate conductivity, measured at 64.4 nano-ohms per meter. Brass terminals have enhanced resistance to wear, adding to the lifespan of lithium batteries.
o Stainless Steel
Stainless steel terminals offer robust physical strength. They resist heat and corrosion, ensuring reliable long-term performance. With 688 nano-ohms per meter resistance, they give stable power transfer in lithium batteries.
o Aluminum Terminals
Aluminum terminals have a unique blend of lightweight and decent electrical conductivity, with 26.50 nano-ohms per meter resistance. In addition, aluminum resists corrosion effectively, boosting terminal durability in lithium batteries.
o Lead Terminals
Lead terminals, with a resistance of 208 nano-ohms per meter, assure steady electrical transmission. Besides, their robust nature withstands physical damage, adding to terminal lifespan. Lead terminals are hence a stable, reliable choice for lithium batteries.
The Significance of Terminal Material in Lithium Batteries!
o Conductivity Level
Lithium battery terminals are vital for battery efficiency. Electricity flows via terminals. Terminals made of brass or nickel show high conductivity. High conductivity means faster charging and better battery performance.
o Corrosion Resistance
The terminal material plays a big role in longevity. Nickel and copper terminals resist corrosion well. A corrosion-free terminal ensures a longer battery lifespan, providing a stable power supply.
o Mechanical Strength
Mechanical strength is crucial for lithium-ion battery terminals. Nickel or steel terminals offer robust durability. Such strength prevents damage during assembly or usage, safeguarding battery function.
o Heat Resistance
Heat can harm battery performance. Terminals made from nickel show good heat resistance. A heat-resistant terminal aids in preventing battery overheating and potential failure.
o Material Cost
Copper, brass, and nickel are common terminal materials. Brass is a cost-effective choice, but nickel offers better performance. Thus, selecting the right material affects overall battery cost.
o Compatibility
The terminal must be compatible with the battery’s other components. Nickel terminals tend to be highly compatible. Greater compatibility means improved battery integration, boosting overall efficiency.
o Safety Concerns
Terminals should also meet safety requirements. Brass or nickel terminals are less prone to sparking. Spark-resistant terminals can help prevent accidents, ensuring safer battery operation.
o Environmental Impact
Environmental factors matter too. Terminals made from recyclable materials like copper can reduce environmental impact. Eco-friendly terminals help to make the battery industry more sustainable.
Accessories for Battery Terminal Connections!
o Terminal Covers
Acting as safety shields, terminal covers help protect against short circuits in lithium battery terminals. Ensuring robust safety, these covers provide reliable insulation.
o Terminal Cleaners
Keeping terminals dirt-free is crucial. Terminal cleaners, with their abrasive surfaces, scrub away build-up with ease.
o Connector Clamps
Linking the battery to the system, connector clamps secure the electrical connection. High-quality clamps ensure reliable power transfer.
o Insulation Boots
Often made of rubber, insulation boots prevent harmful contact. These offer additional safety around high-power terminals.
o Anti-Corrosion Gel
Over time, terminals may corrode. By applying anti-corrosion gel, such corrosion gets halted, enhancing longevity.
o Cable Ties
Helping to organize wires, cable ties promote neatness and prevent tangling. Secure connections are thus more manageable.
o Heat Shrink
For the perfect finish, heat shrink wraps around exposed wire ends. Offering insulation and neatness, it also strengthens the connection.
o Wire Lugs
When connecting cables to terminals, wire lugs ensure a tight fit. High-quality lugs help maintain reliable electrical transfer.
The Process of Connecting Lithium Battery Terminals!

Image Source: lithiumhub.com
o Disconnecting Power
First, always ensure power supply disconnection. Cut-off to Lithium battery terminals minimizes hazards. Circuit breakers, for example, should switch to off. Main plugs Unplugged. Implement safety as a priority.
o Identifying Polarity
Then, recognize terminal polarity. Positive terminals (red) and negative terminals (black) are different. To prevent short-circuits, confirm polarity before soldering lithium battery terminals. Always proceed with caution.
o Securing Terminals
Now, firmly fix terminals. Use suitable fasteners, wrenches, and pliers. Tighten carefully, avoid excessive force. Sturdy connections help battery performance. A job well done means fewer repairs.
o Applying Anti-corrosion
Application of anti-corrosion sprays comes next. Apply a thin layer to terminals. Prolonged lifespan, minimized maintenance are the superb benefits. Use gloves, avoid direct skin contact.
o Attaching Cables
Attach cables following polarity identification. Start with positive, and then move to negative. Secure each using appropriate terminal clamps. Correct cable connections ensure efficient power flow.
o Tightening Connectors
Tightening connectors is crucial. Apply just the right torque, avoid over-tightening. This is to prevent terminal damage. Use torque wrenches for accurate results.
o Testing Connections
After connections, test them. Use a multimeter for voltage checks. Ensure correct readings for battery specification. Unmatched readings indicate connection issues. Handle potential problems immediately.
o Safety Check
Lastly, conduct a safety check. Look for any anomalies – loose connections, corrosion signs. Check for battery leaks too. Reliable checks uphold safety standards. Proper care prevents unwanted incidents.
Maintenance of Lithium Battery Terminals!
o Regular Cleaning
Keeping terminals clean boosts their performance. Regular cleaning prevents build-up, ensuring clear, consistent power flow.
o Corrosion Inspection
Timely checks for corrosion can prevent damage. Through diligent inspections, you’ll enhance terminal longevity.
o Tightness Check
To prevent power loss, checking terminal connections is necessary. A tight fit ensures optimal performance.
o Cable Examination
Regular assessment of cables avoids unexpected power issues. Look for any signs of wear or damage to maintain peak performance.
o Anti-Corrosion Application
By applying lithium grease on battery terminals, the threat of corrosion diminishes. This simple step can make a big difference in longevity.
o Insulation Assessment
Examine insulation for any damage to prevent short circuits. A regular check-up ensures continued safety.
o Load Testing
It’s essential to measure the battery’s capacity to handle loads. Regular testing helps maintain optimal power levels.
o Proper Storage
When not in use, ensure batteries are stored properly. This step protects them from dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
As a reminder, for those wondering what are the three terminals on a lithium-ion battery, they are positive, negative, and a temperature sensor.
Troubleshooting Lithium Battery Terminal Issues!
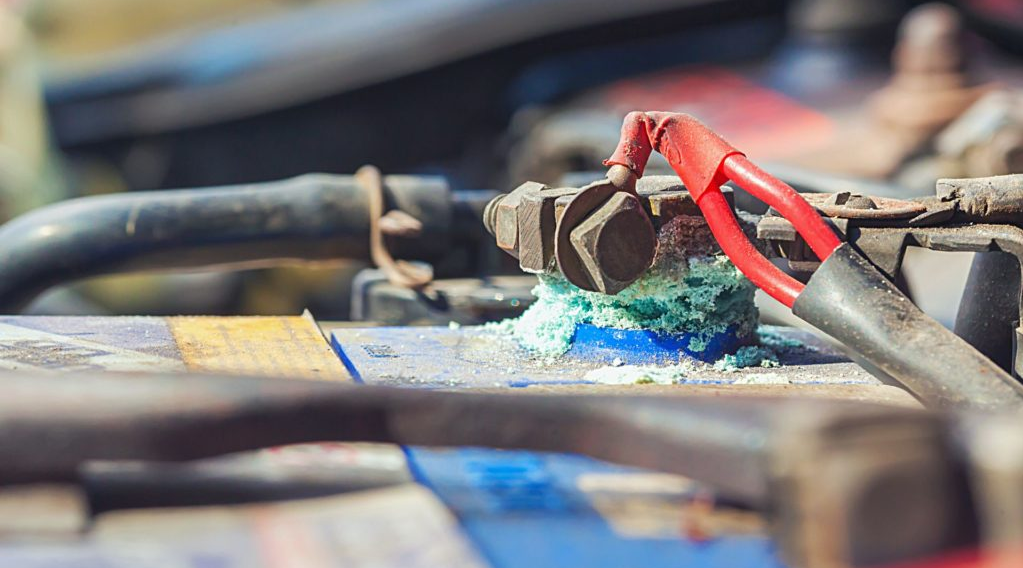

Image Source: battlebornbatteries.com
o Loose Connections
Terminals sometimes become loose. Tighten all battery terminal connectors for accessories to prevent this. Safety is paramount, so handle carefully.
o Corroded Terminals
Corrosion degrades performance. To rectify, clean the terminals regularly. Use baking soda and water, a perfect solution for corrosion removal.
o Damaged Insulation
Insulation safeguards against electric shocks. Check regularly for any damages. If found, replace immediately.
o Overheating Issues
Overheating deteriorates terminals. Maintain a steady temperature by providing adequate ventilation.
o Polarity Mix-ups
Wrong connection can cause a short circuit. Always connect positive to positive and negative to negative.
o Failed Load Test
Conduct load tests regularly. If failure occurs, service the battery immediately.
o Inadequate Power
Inadequate power indicates a failing lithium battery post. When this happens, consider replacement.
o Terminal Pitting
Pitting results from arcing. To prevent this, ensure tight connections at all times.
Tips to Enhance the Lifespan of Lithium Battery Terminals!
o Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance boosts terminal lifespan. Include cleaning, tightening, and corrosion checks in your routine.
o Proper Storage
Store the batteries in cool, dry places. Such conditions slow down chemical reactions, prolonging lifespan.
o Correct Use
Follow manufacturer’s instructions for use. Incorrect usage can lead to battery terminal damage.
o Adequate Ventilation
Ensure enough ventilation around batteries. It helps to avoid overheating, extending the terminal’s life.
o Regular Load Tests
Carry out regular load tests. It helps detect potential terminal issues early.
o Anti-Corrosion Application
Use anti-corrosion sprays on terminals. It wards off corrosive substances, keeping terminals in top shape.
o Insulation Checks
Regularly check terminal insulation. Replace damaged ones promptly to prevent accidental shocks.
o Quality Accessories
Always use high-quality accessories. They enhance terminal performance and lifespan.
Conclusion
From this guide, one grasps the depth of lithium battery terminals. They have types, uses, and needs. Care keeps them working right. Go to buzzupbattery.com. Here, pick reliable terminals for all lithium battery needs. Be smart, choose right, and power up.


